Did you know that weak financial risk management (FRM) was a key factor behind several major bank failures in the past years?
From liquidity crunches to unchecked credit exposure, even small lapses in oversight can trigger massive losses and shake investor confidence.
That’s why FRM has become a strategic necessity, helping institutions turn real-time data into foresight and protect profitability amid market volatility.
In this article, we’ll break down the five key benefits of financial risk management and how it drives stronger compliance, sharper decisions, and lasting financial resilience.
Key Takeaways
- Financial risk management protects stability and profitability
Proactively identifying, analyzing, and mitigating financial threats helps organizations prevent major losses, maintain liquidity, and stay resilient during market volatility.
- Data-driven risk insights enable smarter decision-making
Integrating real-time data and analytics into financial risk management enables leaders to make proactive decisions, transforming reactive strategies into predictive ones.
- Strong compliance builds trust and reduces penalties
Effective FRM ensures regulatory compliance, minimizes exposure to legal and compliance risks, and protects an organization’s reputation with regulators, investors, and customers.
- Operational efficiency and resource optimization follow effective risk control
Streamlined processes, automation, and continuous monitoring not only cut costs but also allow teams to focus on higher-value activities that drive performance and innovation.
- VALID Systems delivers advanced fraud prevention and guaranteed protection
With machine learning–powered tools like CheckDetect and the Edge Data Consortium, VALID helps financial institutions detect fraud in real time, cut losses by up to 95%, and strengthen financial resilience—while offering guaranteed loss coverage for added peace of mind.
What is financial risk management?
Financial risk management is the practice of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats that could compromise an organization’s financial stability.
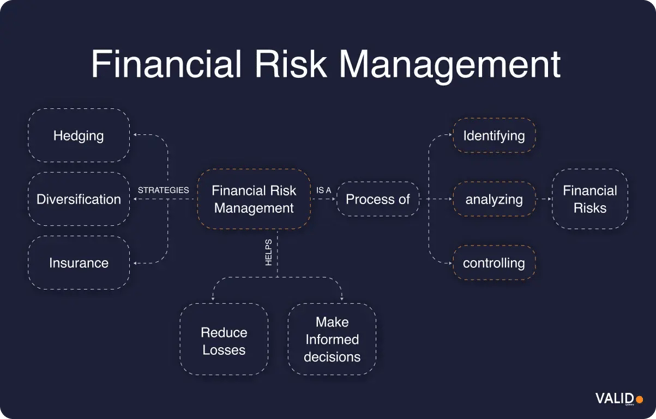
It involves anticipating uncertainties that might affect profits, investments, or overall financial health, and then implementing strategies to mitigate or manage those risks.
Types of financial risks
There are several main types of financial risks that organizations commonly face, each requiring specific strategies to identify, manage, and mitigate potential impacts.
- Operational risk – This risk stems from disruptions in day-to-day operations caused by system failures, human errors, or unforeseen events, which can reduce profitability. While it can’t be fully eliminated, it can be minimized through effective processes, employee training, and contingency planning.
- Credit risk – Credit risk occurs when a borrower or customer fails to meet payment obligations, potentially leading to financial loss. Companies manage this by using credit checks, insurance, and collateral, along with monitoring payment trends and defaults.
- Market risk – Market risk refers to potential losses resulting from changes in market conditions, including interest rates, prices, or geopolitical events. Maintaining a proactive risk management strategy helps organizations remain resilient in volatile markets.
- Liquidity risk – Liquidity risk arises when a company lacks sufficient cash or liquid assets to meet short-term financial obligations. Managing cash flow and maintaining a balanced asset-liability structure are key to reducing this risk.
- Legal or compliance risk – This risk involves potential losses from lawsuits, regulatory penalties, or noncompliance with laws and standards. Integrating legal and compliance oversight within broader financial risk management helps prevent costly violations.
- Foreign exchange (currency) risk – Currency risk results from fluctuations in foreign exchange rates that affect financial performance or asset values. It is often managed through diversification, currency hedging, or the use of financial instruments such as swaps.
5 Benefits of financial risk management
Proper financial risk management comes with a number of benefits that can increase your chances of long-term success, such as:
1. Reduced losses and stronger financial stability
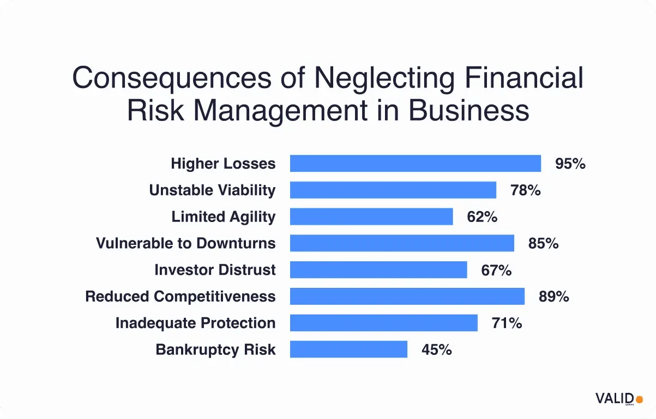
The core purpose of financial risk management (FRM) is to prevent big losses and keep your business financially healthy. When markets swing, liquidity tightens, or unexpected shocks occur, strong FRM practices can help companies avoid major losses.
Effective financial risk management involves several key practices, including:
- Maintaining cash reserves to handle short-term disruptions
- Using insurance and hedging tools (such as currency or commodity hedges) to reduce exposure to market volatility
- Diversifying funding sources to avoid overreliance on a single lender or revenue stream
- Monitoring credit and liquidity risks continuously to catch issues before they become crises
Why it matters:
- Since 2023, at least eight banks have collapsed due to weak financial risk management and poor control of capital and funding.
- In contrast, companies that actively identify, monitor, and hedge financial risks protect their balance sheets and stay resilient in changing markets.
Pro Tip
Many institutions underestimate how much operational inefficiency in fraud review contributes to financial loss. VALID’s CheckDetect helps reduce these losses by detecting and blocking check fraud in real time, across mobile, ATM, and branch deposits.
By automating fraud decisioning and lowering false positives, banks strengthen balance-sheet resilience while freeing teams to focus on higher-value risk analysis.
A top U.S. bank saw a 73% reduction in check fraud losses year-over-year, along with a 40% drop in false positives and 25% faster review times after implementing CheckDetect’s machine learning–driven alerts.

2. Informed planning and strategy
In financial services, the best decisions start with data. That’s the essence of FRM: turning information into insight, and insight into confident action.
When your organization continuously monitors exposures across deposits, fraud alerts, liquidity, and payer behavior, you move from reacting to anticipating. The result is a sharper strategy, smarter forecasting, and greater confidence at every level of the business.
In fact, research shows that 57% of finance and risk teams report improved decision-making when they integrate risk insights and technology into their planning.
With strong FRM, teams can:
- Simulate outcomes under changing market or customer conditions before making operational changes
- Set smarter limits and reserves based on real loss probabilities, not static assumptions
- Detect early warning signals through machine learning that interprets transactional and behavioral patterns
- Align strategy and execution so business growth doesn’t increase risk exposure
Pro Tip
Integrating external intelligence into your risk analysis can dramatically improve forecasting accuracy. For example, through VALID’s Edge Data Consortium, financial institutions gain access to shared, anonymized fraud data across the industry. This helps them detect emerging threats earlier and make more confident strategic decisions based on live behavioral patterns, not assumptions.
3. Stronger compliance and greater trust
Financial risk management gives organizations the structure and visibility they need to stay ahead of regulations while protecting their reputation.
Regulators, auditors, and customers all expect proof that risks are being managed responsibly, from fraud prevention and data protection to anti-money laundering and loan oversight.
A single lapse can mean fines, legal costs, or long-term brand damage. In 2023 alone, financial institutions faced more than $835 million in AML fines.
Strong FRM practices help you:
- Maintain complete audit trails that make reporting seamless and defensible
- Enforce anti-fraud and sanction-screening procedures that protect against costly violations
- Build a culture of accountability and ethics that prevents internal missteps before they reach the public eye
- Automate transaction and customer monitoring so suspicious activity is flagged instantly
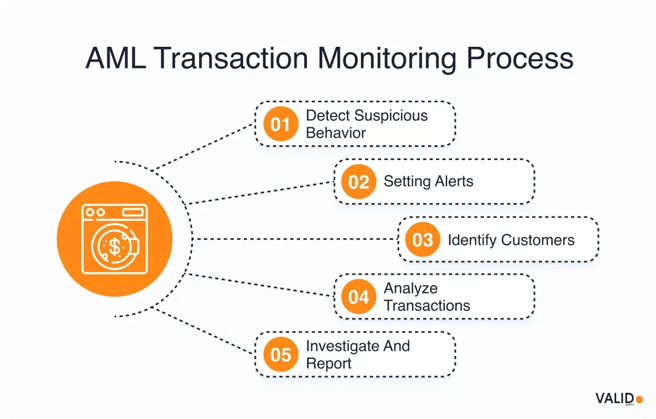
4. Streamlined operations and smarter resource use
FRM isn’t only about preventing losses. It’s about uncovering opportunities to operate more efficiently. By clarifying where risk truly lies, FRM helps leaders focus resources where they matter most and streamline what doesn’t add value.
Stress testing, for instance, can expose structural inefficiencies such as slow approval cycles, duplicated reporting, or policies that quietly erode margins.
Effective FRM can lead to:
- Automated reporting and monitoring that replace time-consuming manual processes
- Streamlined financial systems that reduce redundancy and error
- Cross-trained teams that can pivot quickly when workloads or priorities shift
- Vendor and payment controls that strengthen cash flow and unlock cost savings
5. Strategic growth and innovative opportunity
A mature risk framework gives leadership the confidence to launch new products, enter untapped markets, or explore acquisitions, with a clear understanding of potential outcomes. Rather than holding the business back, FRM becomes the foundation for strategic boldness.
Here’s what the data shows:
- A Harvard Business School–cited analysis found that companies practicing strategic risk management are twice as likely to achieve faster revenue growth.
- Banking leaders report that continuously improving risk systems strengthens resilience and fuels sustainable revenue growth.
How financial risk management fuels innovation:
- Enables organizations to model future scenarios that guide smarter investment and product development decisions
- Allows leaders to plan expansion and borrowing precisely to balance opportunity with risk
- Demonstrates financial discipline that strengthens credibility with investors and lenders
- Directs capital toward high-potential initiatives grounded in data rather than intuition
How does the financial risk management process work?
Understanding financial risk is only the beginning, as you still have to manage it. To increase your chances of doing so successfully, you need to know how the process actually works.
Step 1: Identify risks
A business can only manage the risks it recognizes. This step involves examining all aspects of operations, financial transactions, and market factors that could affect financial health.
Modern tools, such as integrated ERP and accounting systems, can help identify both obvious and hidden risks early by tracking financial data in real-time.
Step 2: Analyze risks
Once risks are identified, it is important to understand their causes and potential impacts:
Both qualitative and quantitative methods can be used to determine whether potential returns justify the risks. For example, calculating the expected loss (Probability × Impact) helps measure the financial exposure and align it with the company’s risk tolerance.
Step 3: Prioritize risks
After analysis, risks should be ranked based on their likelihood and potential impact. High-probability, high-impact risks take top priority, as they pose the greatest threat to financial stability.
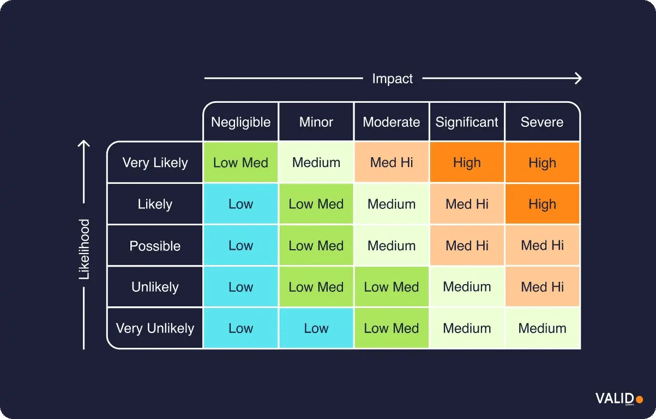
Step 4: Mitigate risks
With priorities set, businesses must take concrete steps to reduce or eliminate key risks. Common mitigation strategies include:
- Diversification
- Hedging
- Insurance coverage
- Stronger internal controls
The best approach depends on the nature of the risk, its potential effect, and the organization’s available resources.
Step 5: Monitor and report
Financial risks are dynamic, so continuous monitoring is essential. Regular tracking and reporting ensure that mitigation strategies remain effective and allow for quick adjustments when conditions change.
Step 6: Review and revise
Finally, businesses should periodically assess the overall effectiveness of their risk management plan. Reviewing results helps identify what worked, what didn’t, and whether new risks have emerged.
This continuous improvement cycle enables businesses to remain agile and resilient as market conditions and internal operations evolve.
The future of financial risk management
As financial risks evolve, institutions can no longer rely on reactive controls or legacy systems. The future of financial risk management lies in real-time intelligence, automation, and industry collaboration, ensuring that threats are identified and neutralized before they impact the bottom line.
That’s where innovators like VALID Systems are leading the charge.
VALID Systems is a financial technology company specializing in fraud prevention and risk management solutions for banks and financial institutions.
Through advanced machine learning, behavioral analytics, and industry data collaboration, VALID empowers organizations to reduce fraud losses, strengthen compliance, and optimize operational efficiency, all while improving customer experience.
How VALID Systems can help you
- Real-time fraud detection – Detect and block check fraud instantly, whether deposits occur via mobile, ATM, or in-branch. This enables proactive control over losses and minimizes operational disruption.
- Reduced losses and false positives – VALID’s CheckDetect technology captures up to 95% of fraud losses while reducing false positives by as much as 40%, helping teams focus on high-risk alerts that truly matter.
- Smarter, data-driven risk decisions – With the Edge Data Consortium, institutions gain access to shared, anonymized fraud data from across the industry, enabling them to identify new threats early and improve forecasting accuracy.
- Operational efficiency through automation – Machine learning–driven decisioning streamlines fraud reviews, shortens investigation times, and reduces manual workload, freeing teams for higher-value analysis.
- Comprehensive fraud coverage across channels – From check fraud and account takeovers to loan application fraud, VALID’s solutions cover multiple threat vectors, providing a unified approach to financial risk management.
- Guaranteed risk protection – VALID’s “Guaranteed Loss Coverage” model absorbs the cost of covered deposit losses, giving financial institutions peace of mind and financial stability.
FAQ:
1. What tools and technologies are used in financial risk management today?
Modern financial risk management (FRM) relies on a mix of advanced tools such as data analytics, artificial intelligence, predictive modeling, and automated monitoring systems.
These technologies help organizations identify, measure, and reduce risks in real time while improving accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making.
2. How can small or mid-sized businesses apply financial risk management?
Smaller organizations can adopt financial risk management by regularly tracking cash flow, diversifying income and funding sources, and setting up strong internal controls.
Using affordable FRM software or dashboards also helps monitor credit exposure, market fluctuations, and liquidity trends, allowing for more informed financial decisions.
3. What are the common challenges in implementing financial risk management?
Typical challenges include limited data visibility, outdated systems, siloed departments, and resistance to change.
Overcoming these challenges requires a leadership commitment, automation, improved data integration, and cross-team collaboration to foster a culture of proactive risk awareness and continuous improvement.
4. How does financial risk management differ from enterprise risk management (ERM)?
Financial risk management focuses specifically on financial exposures, such as credit, liquidity, and market risks. Enterprise risk management (ERM) takes a broader view, addressing all types of risks (strategic, operational, reputational, and compliance) across the entire organization.
