Check Payments: Innovate the Present to Redefine the Future
Unleashing the Power of Checks in the Modern Era of Digital Payments

Introduction
The Growing Market of Non-cash Payments
The world of non-cash payments in the United States has witnessed remarkable growth over the past two decades, as highlighted by the 2022 Federal Reserve Payments Study (FRPS). From 2000 to 2021, the total value of non-cash payments surged 6.5 times, reaching a staggering $129 trillion.
Even though check payments decreased in usage, they still accounted for $27.2 trillion (21% of the non-cash payment ecosystem). This underscores the continued significance of checks in today's digital age.
Since 2000, the average check amount increased by 1.7 times to $2,473 per transaction. From 2018 to 2021, check amounts grew steadily by 1.8%, while the average check amount increased by approximately 30%.1
The white paper embraces the dominance of checks, unlocking its market significance and confronting the rising fraud. It exposes the urgency to transcend outdated techniques and revolutionize security with cutting-edge ML/AI solutions.
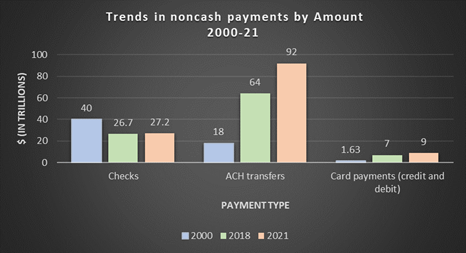
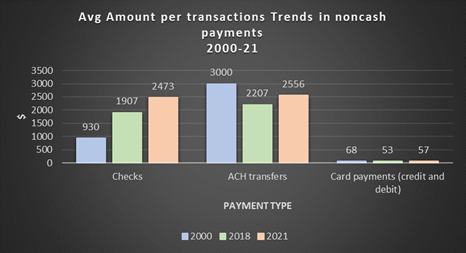
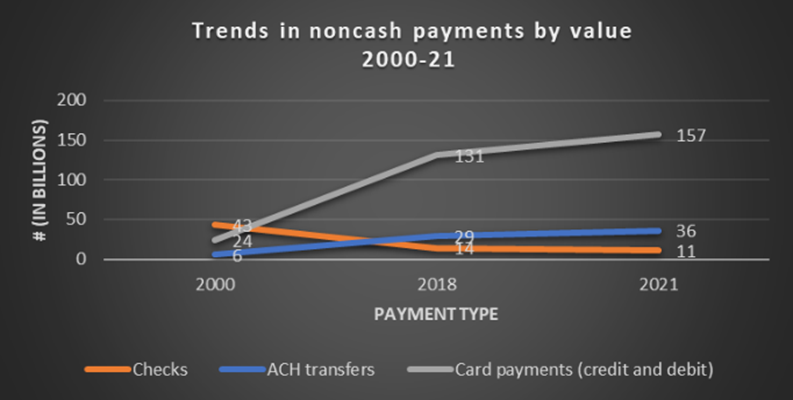
Source: The Federal Reserve Payments Study 2022
Why Are Checks Still Significant?
While many perceive checks as outdated, they continue to hold importance for several reasons:
- Wide Acceptance: Alternative to cash/digital transactions, especially for businesses without electronic payment systems.
- Cashflow: Enables customers, particularly small businesses, to better manage cashflow and take advantage of check float.
- Security: Trackability, ability to stop/cancel checks, offering security compared to cash.
- Business Transactions: Facilitates accounting, record-keeping, commonly used in B2B transactions.
- Personal Preferences: Valued for personal transactions, providing physical proof of payment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Mandated/preferred in real estate, government, or legal transactions.
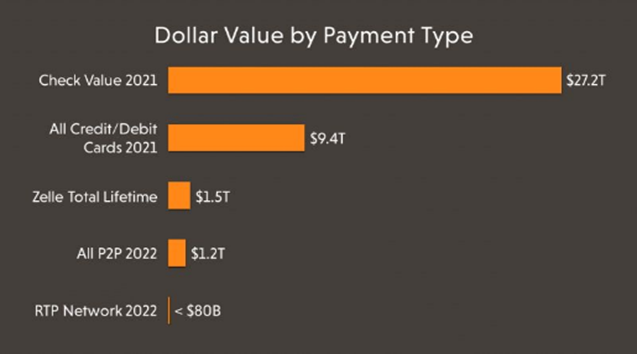
As new payment types have entered the system, investment and mindshare have followed. This along with the perceived death of the check has led to an investment vacuum in the check space for decades, while neglecting the fact that checks represent more dollars than all card, Zelle, and P2P combined.
Processing Cost of Paper Checks
The use of checks poses challenges in terms of processing costs, vulnerability to fraud, and the need for innovation. Physical check transactions are expensive compared to the more cost-effective ACH transactions. On average, physical check transactions cost anywhere from $4 to $20 each while ACH processing ranges between $0.26 to $0.50 per transaction.5 Per FRPS’ 2022 study, there were 11 billion checks and 36 billion ACH transactions. If we consider just the minimum costs, the total cost of processing physical checks is estimated at a staggering $44 billion compared to ~$9 billion for ACH transfers. This massive cost misalignment speaks to the highly manual process still required in the processing of check payments, the inefficiencies that exist, and the potential for innovation within the check process.
Check Fraud is Growing
According to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network, check fraud has increased by ~100% from 2021 to 2022. Check fraud began to increase during the pandemic, when tens of thousands of additional checks were sent via mail, in part due to COVID-19 relief payments and unemployment insurance. The rise of sophisticated fraud techniques like check washing and counterfeit checks necessitates effective countermeasures to safeguard financial institutions and account holders from significant losses.
“The use of paper checks has been declining for decades, yet criminals have been increasingly targeting mailboxes to commit check fraud.”
-The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network, FinCEN6
In 2022, reports of check fraud filed by banks nearly double to 680,000 from 350,000 in 2021. The U.S. Postal Inspection Service, the law enforcement arm of the U.S. Postal Service, received more than 299,000 complaints of mail theft from March 2020 - February 2021, 161% increase from a year earlier.
Types of Fraud
One of the most common approaches of check fraudsters today is check washing. Criminals steal signed checks from postal boxes, then use common chemicals like nail polish remover to remove the dollar amount and the name of the “payee,” or recipient. They rewrite the checks for a new recipient and a larger sum, often hundreds or thousands of dollars more, before cashing the check.
In 2016, the introduction of EMV chip technology led to a new wave of check fraud. Criminals began using advanced print, design, and production technologies to create counterfeit checks that were impossible to detect. During the pandemic, the average mobile check deposits jumped by 41%. This gave fraudsters the opportunity to bypass getting actual check stock as part of their fraud scheme.9
Challenges for Banks
The rise of check fraud in channels promoted by banks is a significant challenge. As digital banking and online payments become more popular, criminals are exploiting these channels for fraudulent activities. This forces financial institutions to balance two competing priorities: driving customer migration of digital tools and channels, while managing risk and losses due to increased fraud. This is most acutely seen within check deposits through mobile devices. Due to the risk and inability to appropriately manage it, financial institutions continue to engineer friction within the customer experience for mobile deposits. This has led to the following hurdles:
- Thresholds related to the amount institutions allow customers to deposit is most limited within mobile deposits
- New customers are either unable to use mobile deposit or suffer from longer funds availability policies
- Standard availability is often most delayed in mobile over other channels, with very few options for instant access to deposits
Removing high-cost transactions at the branch level has been a focus of the banking industry for over a decade. And while the pandemic saw unparalleled migration of check deposits to mobile, and digital adoption broadly, more than 80% of check dollars are still deposited through branches.10
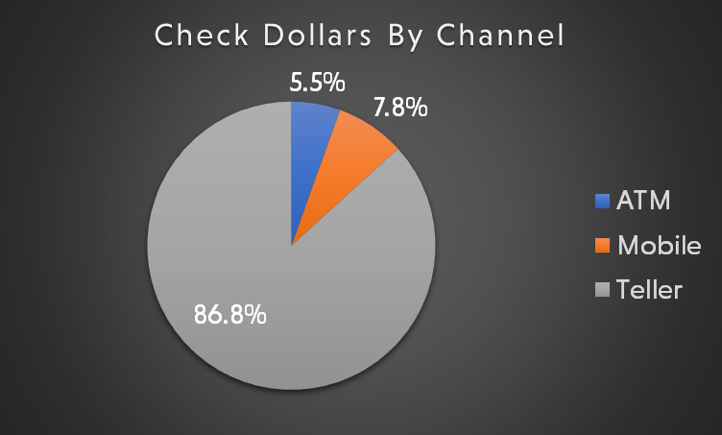
This trend will not be significantly reversed unless existing customer pain-points are addressed in new and meaningful ways. Banks must enhance security, employ fraud detection, educate customers, and balance convenience with robust security measures to combat fraud in these channels, while simultaneously engineering better customer experiences.
Data Limitation in Fraud Coverage
The consortium data platforms offer insights into fraudulent activity and help financial institutions detect suspicious check transactions. Often checks are forged or actual checks are stolen to written off of good accounts with fraud going undetected until days or even weeks later. Fraudsters' evolving techniques further complicate fraud detection.
To overcome these challenges, institutions must invest in improving fraud detection methods, such as ML/AI, and foster collaboration with industry stakeholders. Protecting against check fraud requires a continuous effort to stay ahead of fraudsters and enhance fraud prevention measures.
Traditional Technology
Traditional technologies face challenges in combating check fraud due to new fraudsters employing old tricks. Counterfeit checks, altered checks, and forgery methods have become more advanced, making it harder to detect fraudulent activity. Traditional security features on checks can be replicated or bypassed, making it difficult to rely solely on physical checks for security. The drastic rise in mail theft and check fraud on stolen checks sheds light on another massive gap, check image analysis. With old-fashioned check washing being perpetrated in previously unseen numbers image detection is unable to identify the stolen checks. Check stock, signature, and all other aspects are not detected as fraudulent because they are not fake. Additionally, the time lag in check processing allows fraudsters to exploit the system, necessitating real-time fraud detection mechanisms.
To effectively combat check fraud, a combination of traditional and modern technologies, robust internal controls, and behavior-based risk tools are necessary.
Instant Check Risk Decisioning
To combat the challenges associated with checks and fraud, there is a need for modern solutions. Real-time or instant check processing and behavior-based machine learning check fraud solutions offer significant advantages for businesses, financial institutions, and customers.
These include:
- Real-time funds availability: Instant check processing provides immediate access to funds, enhancing cash flow management and enabling timely financial decisions.
- Behavior-based fraud detection: Cutting-edge ML-based solutions analyze data to detect subtle behavioral cues, identifying fraud in real-time and continuously improving accuracy.
- Enhanced efficiency at reduced costs: Streamlined check verification and clearance processes lead to cost savings and lower administrative overhead.
- Seamless customer experience: Instant processing minimizes delays, offering a frictionless payment journey, and improving customer satisfaction.
- Easy digital banking integration: Effortlessly integrates with digital banking platforms, providing flexibility and convenience to customers for check-related tasks.
- Regulatory compliance: Complies with fraud prevention, privacy, and data security regulations, ensuring peace of mind for financial institutions and businesses.
With these advantages, instant check processing and behavioral machine learning-based check fraud solutions are poised to set a new, stronger standard for modernizing and optimizing check transactions. As businesses and financial institutions embrace these advanced solutions, they can enjoy the benefits of convenience, security, efficiency, and delightful customer experience.

References:
- Federal Reserve. "Payments Study." Retrieved from https://www.federalreserve.gov/paymentsystems/fr-payments-study.htm.
- PYMNTS. "Artificial Intelligence Is Eating the World: How to Avoid Indigestion." Retrieved from https://www.pymnts.com/artificial-intelligence-2/2023/artificial-intelligence-is-eating-the-world-how-to-avoid-indigestion/.
- Red Compass Labs. "FedNow vs. RTP: Can Two Real-Time Payments Systems Coexist in the US Market?" Retrieved from https://blog.redcompasslabs.com/fednow-vs-rtp-can-two-real-time-payments-systems-coexist-in-the-us-market.
- Paystand Blog. "How Much Does It Cost Businesses to Accept Paper Checks?" Retrieved from https://www.paystand.com/blog/how-much-does-it-cost-business-to-accept-paper-checks.
- PaymentCloud Inc. "ACH Fees: The Costs for ACH Processing." Retrieved from https://paymentcloudinc.com/blog/ach-fees/#:~:text=Typical%20flat%20ACH%20fees%20range,the%20costs%20for%20ACH%20processing.
- The New York Times. "Check Fraud Protection." Retrieved from https://www.nytimes.com/2023/03/10/your-money/check-fraud-protection.html.
- CBS News Los Angeles. "On Your Side: Check Fraud Is on the Rise - Here's How to Protect Your Money." Retrieved from https://www.cbsnews.com/losangeles/news/on-your-side-check-fraud-is-on-the-rise-heres-how-to-protect-your-money/.
- American Bankers Association. "Deposit Account Fraud Survey Report - 2019 Edition."
- Jack Henry & Associates. "Why Is Check Fraud So Rampant Again in the U.S?" Retrieved from https://www.jackhenry.com/fintalk/why-is-check-fraud-so-rampant-again-in-the-u.s.
- VALID Systems Financial Institutions Data.